Could Himachal Pradesh Pave the Way for Controlled Cannabis Cultivation?
In a significant move towards embracing modern agricultural practices, Himachal Pradesh has taken a step forward by approving a pilot study on controlled cannabis cultivation. On January 24, the Himachal Pradesh Cabinet greenlit this initiative, spearheaded by two universities, aimed at exploring the medicinal and industrial potentials of cannabis.

What Is Driving This Change?
The decision comes on the heels of a comprehensive study conducted by a committee led by Revenue and Horticulture Minister Jagat Singh Negi. Members of this committee toured several states, including Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir, assessing their successful experience with controlled cannabis cultivation. If the pilot project yields positive results, Himachal Pradesh could become the fourth Indian state to legalize such farming, following Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Jammu & Kashmir. This aligns with international trends, as countries like the US, Canada, and Germany have already sanctioned the controlled use of cannabis.
Understanding Controlled Cannabis Cultivation
Controlled cannabis cultivation refers to the regulated farming of specific cannabis varieties that possess minimal intoxicating properties, known as hemp. Under this framework, the tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) content—the psychoactive component in cannabis—must not exceed 0.3%. The focus of this initiative will be on utilizing cannabis for non-narcotic applications, particularly within the pharmaceutical and industrial sectors. Parts of the hemp plant can be transformed into various products, including textiles, paper, food, cosmetics, and even biofuels. Additionally, compounds like cannabidiol (CBD) present in hemp have been found effective in managing chronic pain.
In April 2023, the Himachal Pradesh government established a committee to examine the legalization of hemp cultivation, excluding charas (a form of hashish), for medicinal, scientific, and industrial uses. Interestingly, cannabis plants are prevalent across all 12 districts of Himachal Pradesh, with regions such as Kullu, Chamba, and select areas of Sirmaur, Mandi, Solan, and Kangra standing out due to their favorable climate for such cultivation.
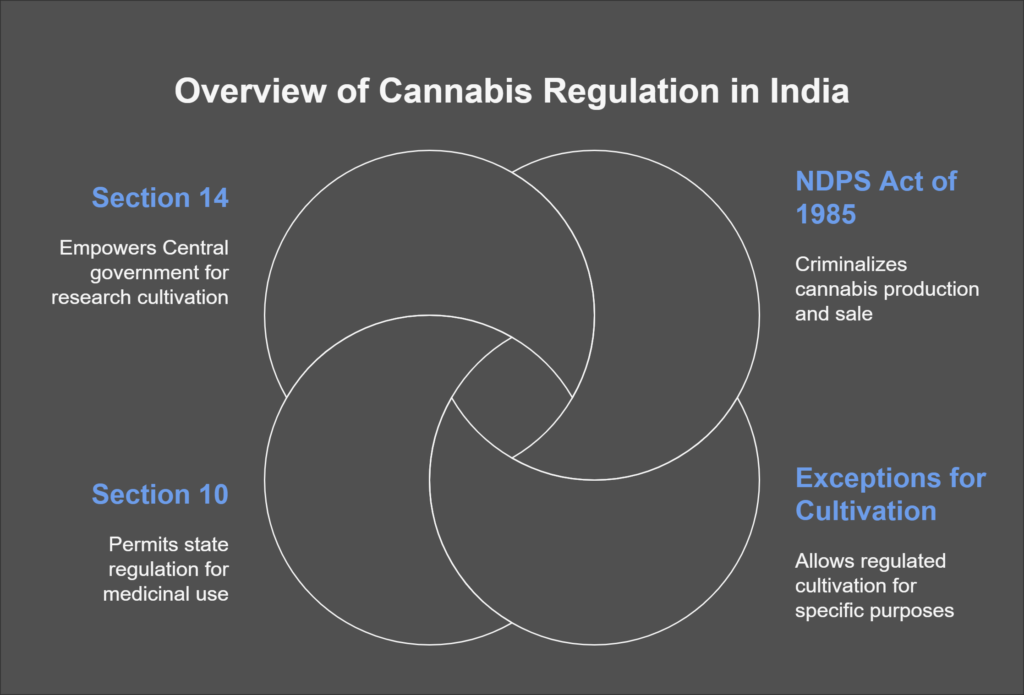
Legal Framework Surrounding Cannabis in India
Currently, cannabis cultivation is largely prohibited in India due to its psychoactive characteristics. The Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act of 1985 criminalizes the production and sale of cannabis resin and flowers. However, the Act does allow for exceptions regarding cultivation and usage for industrial and medicinal purposes, provided there is government oversight.
Section 10 permits state governments to regulate cannabis cultivation for medicinal and scientific ends. Furthermore, Section 14 empowers the Central government to authorize cultivation for research and other sanctioned purposes, thereby providing a pathway for regulated industrial farming.
What Challenges Might Arise in Implementing Controlled Cannabis Cultivation?
While the prospect of legal cannabis cultivation is promising, several challenges have been identified that could impede its implementation. Reflecting on Uttarakhand’s experience as the first state to permit controlled cannabis farming in 2018, the committee highlighted the difficulty in maintaining the mandated THC limit. Obtaining seeds consistently producing plants under this threshold has proven challenging, compounded by issues like cross-pollination.
Furthermore, the initiative will require a concerted effort to raise awareness and provide training for officials and stakeholders. The establishment of specialized laboratories for high-quality seed development and an efficient regulatory framework is also crucial for the success of controlled cannabis farming.
Recommendations for Implementation
The committee’s insights have led to several recommendations aimed at facilitating controlled cannabis cultivation in Himachal Pradesh. These include amending the Himachal Pradesh NDPS Rules, 1985, to allow for cultivation under strict regulations and creating a comprehensive Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) to govern the process. Forming a state-level authority with a single-window system for monitoring and regulating cultivation will also be crucial.
Additionally, research institutions such as CSK HP Agriculture University in Palampur and Dr. YS Parmar University of Horticulture & Forestry in Nauni have been tasked with developing effective research and development techniques to support this initiative. The Legislative Assembly is expected to accept these recommendations soon, setting the stage for a new agricultural frontier in Himachal Pradesh.
Conclusion: What Lies Ahead for Himachal Pradesh and Cannabis Cultivation?
The movement towards controlled cannabis cultivation in Himachal Pradesh holds great potential for economic development and medicinal innovation. With the right regulatory framework, research support, and community engagement, the state could transform its agricultural landscape while adhering to legal and safety guidelines. As the pilot study unfolds, it will be crucial to monitor its progress and address the challenges that may arise to ensure a successful implementation of this progressive initiative.
Post a Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.


